Published: 2 April 2012
Computer power stacks up for flood mitigation
Carrie Bengston
The best tools to mitigate the effects of floods such as those we’ve seen recently literally splashed across our TV screens may not be levies or sandbags, but computers.
|
|
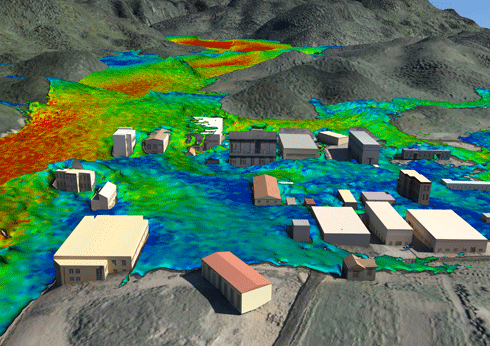
CSIRO’s computational fluid modelling expertise has enabled Chinese authorities to visualise what would happen if one of their largest dams – Geheyan – were to fail, sending 3.12 billion cubic meters of water crashing onto the town below. The colours denote different floodwater velocities. Credit: CSIRO
|
Wee Waa, Moree and Wagga Wagga – towns that to many people have previously been just dots on maps – recently made headlines, for all the wrong reasons. TV news footage showed these towns deluged with murky water from rivers swollen by record downpours. Residents, emergency services and local mayors could only assess the damage and do the best they could as they waited for damaging flood waters to recede.
While floods like this will always occur, it is possible for agencies and communities to prepare and respond more effectively. Computer power is the key: it can model fluids such as flood waters incredibly accurately. Data about specific landscapes and regions can be combined with mathematical equations of how fluids behave and move, helping emergency managers, town planners and even insurance companies be prepared for future floods.
The data deluge in sciences such as environmental modelling is every bit as awesome as the real-life deluges experienced recently in NSW. Resource managers and planners are beginning to take notice of the power of computational fluid modelling for understanding and analysing vast amounts of environmental data, and for predicting changes due to floods. Computer modelling power is based on both the power of computers themselves and the power of the algorithms (computer processing steps) that run on computers.
Twice each year, the world’s fastest supercomputers are ranked in the ‘Top500 list’. A standard test called the Linpack benchmark compares computers' speeds and energy consumption. Computer owners such as universities and government data centres, technology companies such as Intel, and supercomputer geeks all eagerly await the latest list.
In November 2011, for the first time, the number one computer on the list – Japan’s ‘K computer’ – clocked in at more than 10 petaflops, doing more than 10 quadrillion calculations per second.1
Less than three years ago, these speeds were unimaginable. Every ten years, supercomputers speed up about 1000 times. (This acceleration in processing power eventually makes its way to our desktops, mobile phones and other devices.)
|
|
The head of CSIRO’s computational and simulation sciences team, Dr John Taylor, leads teams of researchers with expertise in statistics, mathematics, information and communication technologies and other areas of science. The teams analyse large datasets from huge sensor networks such as radio telescopes, large experiments such as those using the synchrotron, and high-throughput DNA analysis systems. Credit: CSIRO
|
CSIRO’s greenest supercomputer – a relatively new type of supercomputer called a graphics processing unit (GPU) cluster – has made the Top500 several times since its launch in November 2009. It ranked 212 in the November 2011 list.
Located in Canberra, it’s one of the world’s fastest and least energy-hungry supercomputers. Intriguingly, the GPUs at its heart started out as graphics rendering hardware for computer games. So, it’s no surprise that the cluster – now a workhorse for many scientists in CSIRO – can produce informative and stunning animations as it rapidly crunches enormous numbers of numbers.
‘In recent years, the huge increase in computer power and speed, along with advances in algorithm development, have allowed mathematical modellers like us to make big strides in our research,’ says Mahesh Prakash of CSIRO's computational modelling team, led by Dr Paul Cleary.
‘Now, we can model millions, even billions of fluid particles,’ says Dr Prakash. ‘That means we can predict quite accurately the effects of natural and man-made fluid flows like tsunamis, dam breaks, floods, mudslides, coastal inundation and storm surges.’

|
|
Dr Mahesh Prakash is one of a team of computational modellers at CSIRO who’ve clocked up several decades of work on fluid computer models and algorithms, including rendering to create ‘real life’ 3D wave and flood effects. Credit: CSIRO
|
A dam break, for example, is essentially a human-made flood. Like a flood caused by excessive rainfall, a dam break can be modelled on computer.
The models create colourful and detailed animations that show how rapidly the water moves and where it goes: where it ‘overtops’ hills and how quickly it reaches towns or infrastructure such as power stations. This information can help town planners plan structures such as levies and help emergency services respond more efficiently.
CSIRO’s dam break models have been validated using historical data from the St Francis Dam break, which occurred in California in 1928 and killed more than 400 people. Dr Prakash and his team have used the validated modelling techniques for a range of ‘what-if’ scenarios for other dams.
Working with the Chinese Academy of Surveying and Mapping, the CSIRO team simulated the hypothetical collapse of the massive Geheyan Dam: one of the world's biggest. CSIRO combined their unique modelling techniques with digital terrain models (3-D maps of the landscape) to obtain a realistic picture of how a real-life disaster might unfold.

|
|
Realistic animations help flood mitigation and emergency response groups to better manage disasters. Credit: CSIRO
|
These evidence-based fluid-modelling tools can also help decision makers manage dam operations during excessive rainfall, for example, allowing them to determine when to undertake controlled water releases and how much water to release.
The future of computer modelling of floods and other natural disasters can only improve as computers and algorithms become more powerful. CSIRO's own supercomputer arsenal will be given a boost when its GPU cluster is upgraded this year. The tender was won by Xenon Systems of Melbourne and the upgrade is currently taking place.
The leader of CSIRO’s computational and simulation sciences team, Dr John Taylor, says the upgrade will open up even more possibilities.
‘We're anticipating a significant boost in computational performance and greater compatibility with the next generation of accelerator cards, all achieved using less energy per calculation,’ says Dr Taylor.
Flood modellers, regional planners and emergency managers – watch this space!
View a clip on computational fluid modelling for disaster management here.
1 In supercomputing, flops – or more accurately, flop/s, for floating-point operations per second – is a measure of a computer's performance, especially in fields of scientific calculations that rely on floating-point calculations. The prefix ‘peta’ denotes 1015 or 1 000 000 000 000 000 flops.








